Understanding the Climate Conundrum: Cool Coastal Summer vs. Anomalous Inland Heat
Amidst the typical seasonal patterns of California, an unexpected climatic scenario has surfaced this summer as coastal areas experience an unusually cool season contrasted by scorching temperatures inland. This phenomenon raises significant questions regarding the impact of regional climate variations and broader climate change trends.
What’s Behind the Cool Coastal Summer?
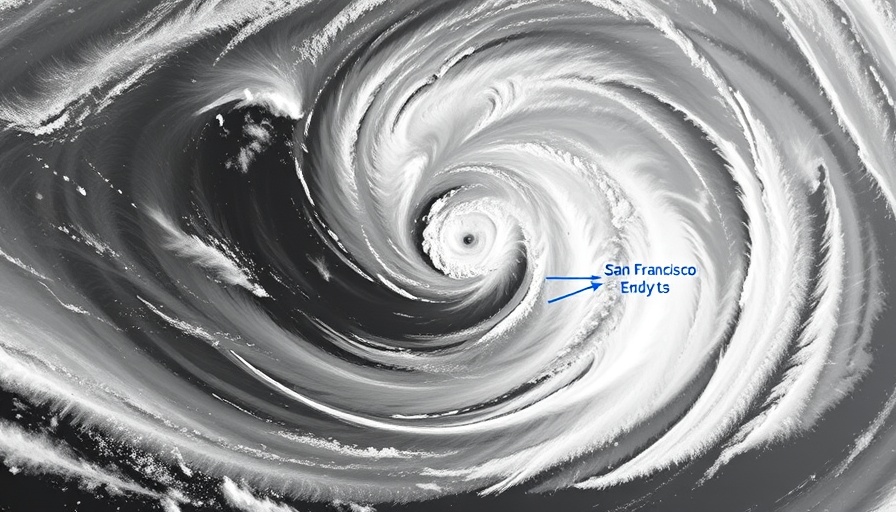
From May through mid-July, Northern and Central California’s coastal regions—including cities like San Francisco and Monterey—have reported some of the coolest conditions in decades, with persistent marine layers, overcast skies, and strong winds setting the tone for a season that, for many locals, is characterized by an enduring chill. These weather trends, which have seen June temperatures hit lows reminiscent of the early 20th century, demonstrate the complexities of climate change, particularly in a state known for its temperate summers.
Heat Waves Bucking the Trend: Inland Temperature Surges
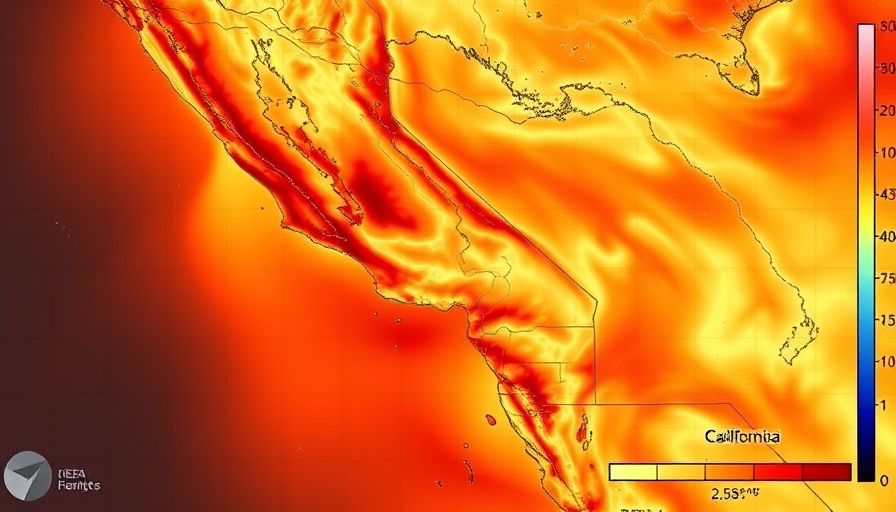
In stark contrast, areas well inland, including parts of the Sacramento Valley and the Sierra Nevada foothills, have recorded blistering heat, with temperatures reaching nearly record highs. Such dramatic variations underscore the atmospheric “thirstiness”—a phenomenon driven by diminished moisture levels resulting from higher evaporation rates. This contradiction between climates across short distances brings to light crucial considerations about regional microclimates and their implications for agriculture, wildlife, and local ecosystems alike.
The Role of Climate Change in Daily Weather Patterns
Research indicates that while annual temperatures across California have steadily increased, the impact of climate change appears to be less pronounced along the coast regarding early summer months. Many areas along the northern and central coastline have shown minimal warming in comparison to their inland counterparts, where substantial temperature increases have occurred over the past four decades. This finding illustrates the concept of 'shifting baseline syndrome,' as older generations perceive climatic shifts through a narrow lens of their recent experiences.
A Deeper Dive: Historical Context and Future Predictions
Understanding the historical context of weather patterns is essential to grasp the implications of present-day anomalies. Californians have experienced fluctuating weather conditions across decades, often punctuated by extremes. As climate models adjust, urban planners, policymakers, and residents must prepare for these changes. Predictive models suggest that the increased frequency of such contrasting weather conditions may lead to pressing challenges in managing local resources, such as water and energy supply, and addressing the impacts on vulnerable communities.
Final Thoughts: Understanding How Climate Affects Our Lives
As we navigate the complexities of climate change, it is crucial for Californians to remain informed and engaged with their local environments. Recognizing the varying implications of weather patterns—particularly how they contrast across different regions—can help residents, businesses, and policymakers make more informed decisions that align with changing natural conditions. Taking action to mitigate climate impacts starts with awareness, advocacy, and adaptability.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment